What Determines Motor Life?
Understanding how to use a product correctly can significantly impact its performance and longevity. For instance, maintaining cast iron pans appropriately can extend their lifespan. Similarly, electric motors require knowledge of the key factors affecting their lifespan to ensure prolonged use and cost savings in the long term.
First, what defines the end of life?
Typically, end of life refers to when a product stops functioning as expected. But what does this really mean?
End of life occurs when the motor’s speed, torque, accuracy, and other specified parameters can no longer be achieved. Even though the motor may still operate, it won’t meet its intended specifications. When a product can’t perform its intended function, it’s effectively useless to us.
Â
Â
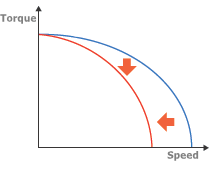
As a motor wears over time, its torque and speed will naturally decline as it approaches its end of life.
Â
What are the primary factors impacting lifespan?
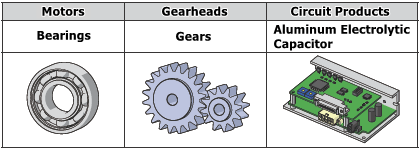
A product’s lifespan is often determined by the first component to fail. In electric motors, the three main components most susceptible to failure are the bearings, gears, and circuitry, including drivers and controllers.
Â
Â
Bearings
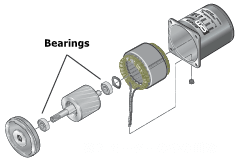 |
Bearings are essential mechanical components that limit unwanted motion and reduce friction between moving parts. In a motor, they support the load shaft and rotor. Any damage to the bearings can halt the motor's operation, making them critical components. |
|
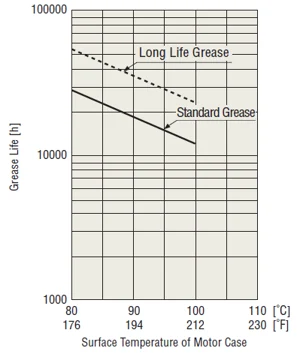
Standard motor operating life is estimated based on bearing grease life, which is heavily influenced by temperature. Exceeding motor specifications, such as radial (overhung) load and axial (thrust) load, can also lead to a shorter lifespan. Motors equipped with long-life bearing grease can operate for approximately 10,000 hours. |
 |
Â
Gears
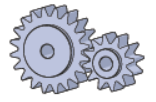
Gears are used to reduce motor speed while increasing torque. Torque is multiplied by the gear ratio between the gears (and gear efficiency), and speed is reduced by the gear ratio. Like bearings, gears handle the load directly and can wear out over time, especially under impact loads or when motor specifications are exceeded. Once worn, the motor can still function, but it will produce excessive noise and backlash, failing to meet its specifications.
Â
Circuit Products
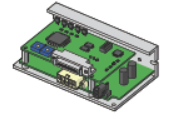
Circuit products include drivers, which supply logic and current to stepper or servo motors, and controllers, which provide logical instructions to the driver. Components within circuit products, such as electrolytic capacitors, can fail due to high temperatures. The lifespan of a circuit product depends on the lifespan of its electrolytic capacitor.
Â
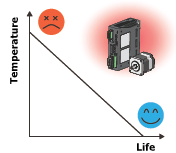
| TIP: How does temperature specifically impact lifespan? | ||
|
Â
How can we control temperature rise?
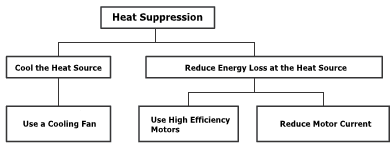
There are two main ways to manage temperature rise: cooling the heat source and reducing the amount of heat generated by the heat source. To cool the heat source, you can use a cooling fan, heat radiation (mounting to a larger Metal Plate, heat dissipation), and other methods to lower the temperature. Reducing the operating temperature of motors extends their lifespan since the bearing grease lasts longer. Lowering the operating temperature also increases the motor’s duty cycle. In one project, I supported the implementation of a water-cooled jacket to nearly double the stepper motor’s duty cycle to around 100%.
The other approach is to minimize energy loss at the motor. Since energy loss manifests as heat, reducing energy loss also reduces temperature. This can be achieved by using high-efficiency motors or continuous-duty motors. For stepper and servo motors, reducing the motor current decreases its operating temperature. Current is directly proportional to temperature, but it’s also proportional to torque, so it’s best to reduce the current to a level that still provides sufficient torque while minimizing temperature.
Â
Â
Thank you for reading, and please consider subscribing.
For more information on how temperature affects service life, rated life for different products, and how to calculate service life, here’s a section from our technical reference in the catalog that goes into further detail.
Â
 hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(2284573, '37366249-cf39-4d82-b445-cf0ca1d9d6a6', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(2284573, '37366249-cf39-4d82-b445-cf0ca1d9d6a6', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
Â
Interested in our cooling fans, high-efficiency motors, or methods to reduce current?
Please contact our knowledgeable technical support engineers.
Â
"Frame,Size and Figure Customized,Welding is Close Seam,Brushed Nickel Surface Treatment
Changzhou Fuku Precision Machinery Co., Ltd. , https://www.fukuindustrial.com